Leptin: the hormone that suppresses appetite
Many dieters struggle with weight loss because of their feelings of hunger. They try to lose weight but their appetite gets in the way. Many have tried unsafe fad diets that are based on science but do not fully understand the science behind them. Recently, I wrote an article on ghrelin. Ghrelin is also known as the “hunger hormone.” Leptin is the yin to ghrelin’s yang. The name leptin comes from the Greek word “leptos” which translates as “thin.”
Leptin the appetite
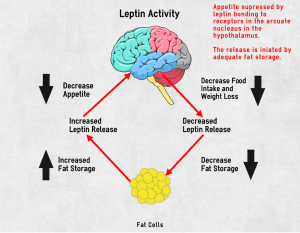
Leptin is often called the “satiety hormone” or the “starvation hormone.” It was first discovered in 1994. It is released from adipose (fat) cells. The function of leptin is to regulate energy balance or homeostasis1. Basically, leptin is a thermostat for fat storage. If fat storage is at an adequate level, leptin signals a need to suppress your appetite2,3,4, and leptin is released from your fat cells. I look at this as sort of similar but opposite to ghrelin being suppressed by a full stomach. With leptin, a release is increased by swollen, fat-rich adipose cells.
Leptin is released from fat but it signals a feeling of fullness in a part of the brain called the hypothalamus. In other words, the hormone acts on the hypothalamus to induce satiety or to control appetite based on the level of energy stores in fat cells. As fat weight is lost, leptin release lowers5,6, and as weight is gained, leptin release increases. If you look at the hormone physiology cycle above, you will note as fat storage increases, fat cells increase leptin release which suppresses hunger in the hypothalamus and you eat less. As your body starves or loses weight, leptin release reduces and appetite should return due to ghrelin hormone release from the stomach.
The physiology of leptin is not as straightforward as one might guess. Although leptin suppresses appetite, it does not work as well in obese individuals. In obese individuals, the subjects develop a decreased sensitivity to leptin which results in a decreased signal of satiety despite adequate energy stores7. This is similar to the resistance to insulin in type 2 Diabetes. When there are adequate fat stores in the obese subjects, leptin resistance or decrease sensitivity makes your hypothalamus less sensitive to leptin so higher levels are required to suppress appetite and create a full feeling.
How do I Increase my Leptin?
- Get adequate sleep8,9,10,11.
- Stress management. Research is mixed on leptin but it helps with cortisol levels and hunger.
- CPAP – if you have sleep apnea. Although research is not clear, it may help with reducing hunger.
- Interval or burst training. The research is mixed, but it does help with weight loss and lowers ghrelin.
- Avoid high fructose corn syrup and sugar12,13.
So, you may ask, why does any of this matter? This matters because if you understand how leptin works and what can raise or lower leptin levels, you understand what to do and what not to do. Simply put, the physiology behind leptin explains why we gain weight and why we need to do everything we can to avoid worsening our leptin resistance.
Are there any drugs to help me with this? Yes and no. There is no magic bullet to help raise your leptin levels, but there are some simple things you can do to raise your leptin or reduce your leptin resistance. Plain and simple, adequate sleep will improve your response to and levels of leptin. Also, higher protein intake and fish oil will help not only raise leptin levels but also reduce ghrelin. Until the day when we can find a grueling agonist that works to suppress hunger, these recommendations are all we have to increase leptin levels and suppress hunger.
Recommendations:
- Moderate exercise for 30 minutes 5 days per week. This helps with both weight loss and hunger but the research is mixed on leptin levels.
- Get 7-8 hours of sleep each night10,11,8,9.
- Adequate protein intake (1 mg per Kg body weight)14. Although research is proven that leptin decreases on a high protein diet, higher protein diets decrease appetite. Although there is no scientific proof at this time, I surmise that this must be done to decrease leptin resistance.
- Add fish oil supplementation15.
- Avoid high fructose corn syrup and sugar12,13.
- Manage your stress. Research is mixed on leptin but it helps with cortisol levels and hunger.
References
-
1.Brennan A, Mantzoros C. Drug Insight: the role of leptin in human physiology and pathophysiology–emerging clinical applications. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2006;2(6):318-327. [PubMed]
-
2.Friedman J. Leptin, leptin receptors, and the control of body weight. Nutr Rev. 1998;56(2 Pt 2):s38-46; discussion s54-75. [PubMed]
-
3.Friedman J, Halaas J. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature. 1998;395(6704):763-770. [PubMed]
-
4.Friedman J. The function of leptin in nutrition, weight, and physiology. Nutr Rev. 2002;60(10 Pt 2):S1-14; discussion S68-84, 85-87. [PubMed]
-
5.Dubuc G, Phinney S, Stern J, Havel P. Changes of serum leptin and endocrine and metabolic parameters after 7 days of energy restriction in men and women. Metabolism. 1998;47(4):429-434. [PubMed]
-
6.Chin-Chance C, Polonsky K, Schoeller D. Twenty-four-hour leptin levels respond to cumulative short-term energy imbalance and predict subsequent intake. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(8):2685-2691. [PubMed]
-
7.Pan H, Guo J, Su Z. Advances in understanding the interrelations between leptin resistance and obesity. Physiol Behav. 2014;130:157-169. [PubMed]
-
8.Collet T, van der, Henning E, et al. The Sleep/Wake Cycle is Directly Modulated by Changes in Energy Balance. Sleep. 2016;39(9):1691-1700. [PubMed]
-
9.Taheri S, Lin L, Austin D, Young T, Mignot E. Short sleep duration is associated with reduced leptin, elevated ghrelin, and increased body mass index. PLoS Med. 2004;1(3):e62. [PubMed]
-
10.Pejovic S, Vgontzas A, Basta M, et al. Leptin and hunger levels in young healthy adults after one night of sleep loss. J Sleep Res. 2010;19(4):552-558. [PubMed]
-
11.Schmid S, Hallschmid M, Jauch-Chara K, Born J, Schultes B. A single night of sleep deprivation increases ghrelin levels and feelings of hunger in normal-weight healthy men. J Sleep Res. 2008;17(3):331-334. [PubMed]
-
12.Bray G, Nielsen S, Popkin B. Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup in beverages may play a role in the epidemic of obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79(4):537-543. [PubMed]
-
13.Stanhope K, Havel P. Endocrine and metabolic effects of consuming beverages sweetened with fructose, glucose, sucrose, or high-fructose corn syrup. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;88(6):1733S-1737S. [PubMed]
-
14.Weigle D, Breen P, Matthys C, et al. A high-protein diet induces sustained reductions in appetite, ad libitum caloric intake, and body weight despite compensatory changes in diurnal plasma leptin and ghrelin concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;82(1):41-48. [PubMed]
-
15.Ramel A, Martinéz A, Kiely M, Morais G, Bandarra N, Thorsdottir I. Beneficial effects of long-chain n-3 fatty acids included in an energy-restricted diet on insulin resistance in overweight and obese European young adults. Diabetologia. 2008;51(7):1261-1268. [PubMed]










Be the first to comment on "Leptin the Appetite Suppressor Hormone"